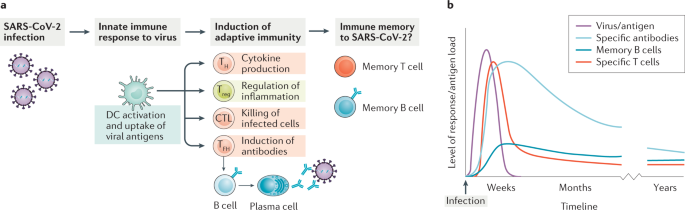
Research shows T cell response and antibody immune response are independently correlated to protection against SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis of the study cohort evaluated overlap between the two test methods.
 The Search For Immune Responses That Stop Covid 19 The Scientist Magazine
The Search For Immune Responses That Stop Covid 19 The Scientist Magazine
Serum samples were collected monthly to measure antibody levels and blood samples were taken after six months to measure the T cell response using an ELISPOT and ICS analysis.
T cell response. They found that a strong SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell response was predictive of milder infection. Follicular helper T cells. The findings indicate that T cells are more important in the bodys fight against Covid-19.
They recognise and bind to the antigens expressed by pathogens via MHC I molecules. Memory T and B cells. Germinal center B cells.
Study documents 2 cases of reinfections in India but experts say data doesnt offer insight. In the new study by UK Coronavirus Immunology Consortium and the University of Birmingham T-cell responses were reported in 31 per cent of recipients of the AstraZeneca vaccine and 12 per cent of. The research paper highlighted that two doses of the Pfizer vaccine had triggered a strong T-cells response against the UK and South African mutation of the coronavirus the Guardian.
T cell responses could also help to explain why some people recover relatively quickly from COVID-19 but others continue to suffer chronic after-effects for months following infection. Upon binding to the antigenpathogen the cytotoxic T cell releases a variety of mediators to destroy the pathogen. Adaptive T cell Immune Response The cytotoxic T cells help with pathogen removal.
CHICAGO Reuters - A critical component of the immune system known as T cells that respond to fight infection from the original version of the novel coronavirus appear to. Each viral pathogen has unique frequently nuanced aspects to its replication which affects the host response and as a consequence the capacity of the virus to produce disease. However for many infectious diseases T cells are an important part of naturally acquired protective immune responses and inducing these by vaccination has been the aim of much research.
T cells must recognise foreign antigen strongly and specifically to mount an effective immune response and those that do are given survival signals by several molecules including ICOS 4-1BB and OX40. However the T cells of asymptomatic individuals produced greater amounts of two proteins called IFN-γ and IL-2. In some cases such as the South Africa variant T-cells produced a nearly equal response to the.
These molecules are found on the T-cell surface and are stimulated by their respective ligands which are typically found on APCs. Responses decreased at most 30 relative to that cells response to the SARS-CoV-2 wild type. Antibody response represents half of the immune system and T cells are the other half.
These T cells may function as effector cells or may orchestrate propagation of the inflammatory response and cellular recruitment through their secretion of cytokines and chemokines. The lack of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies with mild clinical disease suggests an important role of T-cell response in defense against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell-mediated immunity CMI cellular immunity.
The study found that virus specific T cells were detectable in all donors at six months. The T cell response is an integral and essential part of the host immune response to acute virus infection. To find out more we spoke to Professor Rosemary Boyton RB and Professor Danny Altmann DA who recently published a paper in Science Immunology on what we know so far about T cell immunity.
Immune responses mediated by activated antigen-specific T lymphocytes. T cells work by killing infected host cells and activating other immune cells producing cytokines and controlling the immune response.