People with this disease often have progressive loss of the fatty covering myelin that surrounds the nerves in the brain and spinal cord. X-linked disorders result from mutated genes on the X chromosome.
 Definition Of X Linked Recessive Inheritance Nci Dictionary Of Genetics Terms National Cancer Institute
Definition Of X Linked Recessive Inheritance Nci Dictionary Of Genetics Terms National Cancer Institute
Humans and other mammals have two sex chromosomes the X and the Y.

X linked genetic disorders. However the Y chromosome doesnt contain most of the genes of the X chromosome. The scales of X-linked ichthyosis are often dark and usually cover. Females inherit two X chromosomes with males inheriting just one.
Their expression in females and males is not the same. Males have one X and one Y. There are several X-linked or sex-linked recessive genetic disorders hemophilia muscular dystrophy which are inherited through a genetic defect on an X chromosome.
One X chromosome is inherited from each parent XY. Genes on the X chromosome are said to be X-linked. X-linked ichthyosis is a disorder in which the skin cells are produced at a normal rate but they do not separate properly at the surface of the stratum corneum the outermost layer of the skin.
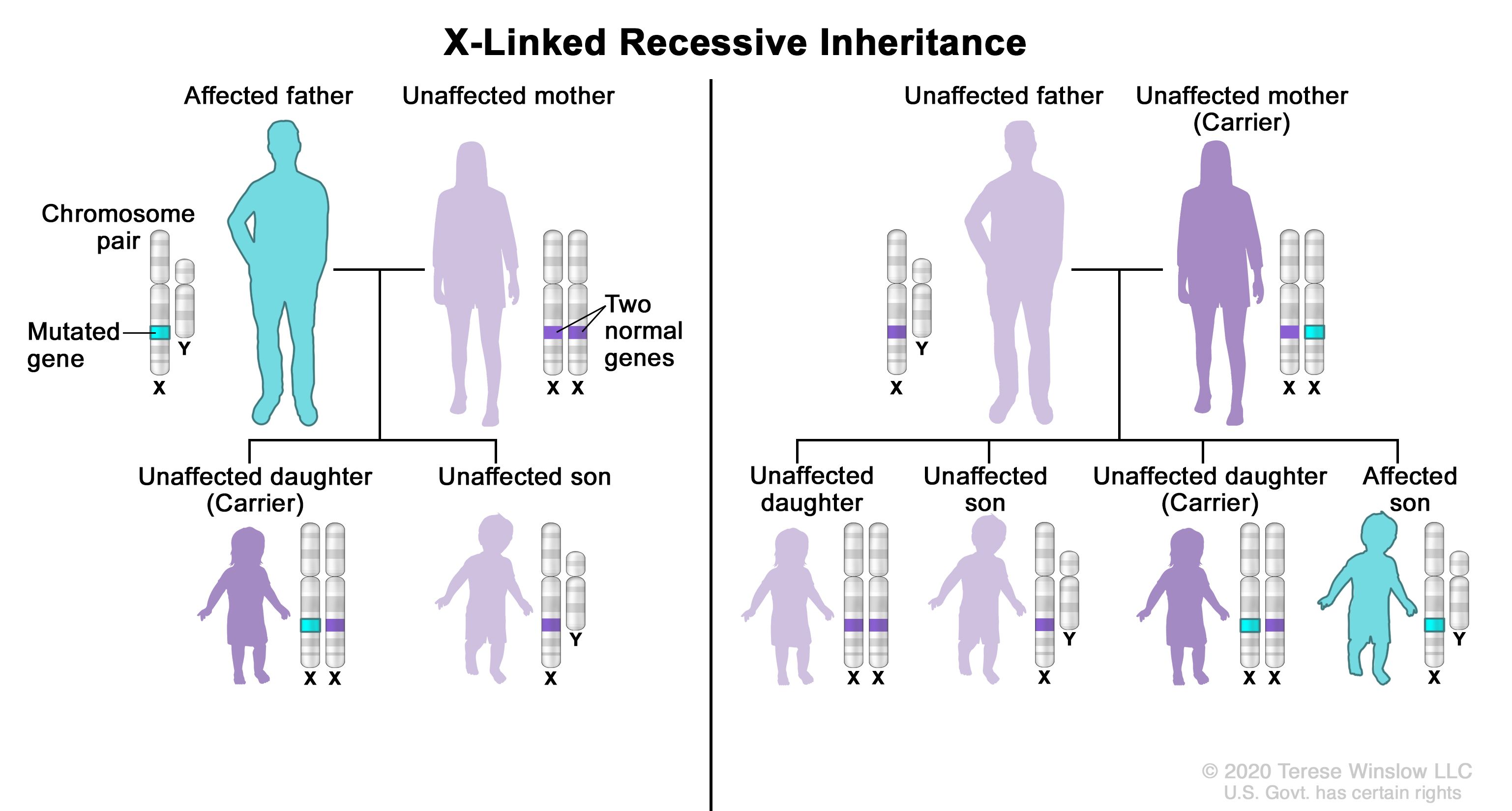
X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Genes on the X chromosome can be recessive or dominant. Males have one X chromosome.
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy X-ALD is a genetic disease that affects the nervous system and the adrenal glands small glands located on top of each kidney. There are around 4000 known inherited conditions that are caused by a difference in a single gene and a number of these follow an X-linked pattern of inheritance. X-linked recessive diseases most often occur in males.
On the other hand females who have two X chromosomes will be carriers of the defect in the majority of cases and so they are usually asymptomatic. An X-linked genetic disorder is one caused by a mutation change in a gene on the X chromosome. This represents the sex chromosomes of a female.
A male has an X chromosome from his mother and a Y chromosome from his father. Cell-cloned pigs from male cells with mutations in an X chromosomal gene is a reliable and straightforward method for reproducing X-linked genetic diseases XLGDs in pigs. The three best-known disorders which seem to be inherited in this way are incontinentia pigmenti IP Bloch-Sulzberger oral-facial-digital I OFD I syndrome and focal.
The key difference between X linked dominant and X linked recessive is that X linked dominant is a genetic disorder caused due to a dominant mutant gene located on the X chromosome while X linked recessive is a genetic disorder caused due to one or two recessive mutant genes located on the X chromosomes. It causes progressive muscle weakness and starts to affect boys when they are toddlers. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy DMD is an X-linked recessive condition.
X-linked is a trait where a gene is located on the X chromosome. X-linked genes have distinctive inheritance patterns because they are present in different numbers in females XX and males XY. Describes a gene on the X chromosome.
In an X-linked or sex linked disease it is usually males that are affected because they have a single copy of the X chromosome that carries the mutation. Females have two X chromosomes. However the severe symptoms of XLGDs are often accompanied by impaired growth and reproductive disorders which hinder the reproduction of.
Because of that it doesnt protect the male. X-linked genetic diseases therefore affect males and females differently. Females have two X chromosomes.
Males have no spare X chromosome to revert to if. Patients with XLH have inactivating mutations in the PHEX gene which encodes phosphate-regulating neutral endopeptidase PHEX with many different mutations of. X-linked human genetic disorders are much more common in males than in females due to the X-linked inheritance pattern.
Males have only one X chromosome. The X-linked dominant disorder X-linked hypophosphatemia XLH is the most common form of inherited hypophosphatemia. In fact feasible production of model pigs reproducing XLGDs such as severe combined immunodeficiency SCID 8 9 Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD 10 and hemophilia 11 has been reported.
Nuclear transfer using male cells carrying mutations in an X chromosomal gene enables the direct cell-to-animal generation of models for X-linked genetic diseases XLGDs. X-linked dominant inheritance with lethality in hemizygous males is a rare mode of inheritance. Males who have only one X chromosome ie they are hemizygous will fully express an X-linked disorder.
The Y chromosome is the other half of the XY gene pair in the male. This slows the rate of shedding of the skin cells resulting in a build-up of scales. A single recessive gene on that X chromosome will cause the disease.
This represents the sex chromosomes of a male. A female has 2 X chromosomes one she inherited from her mother and one she got from her father.

/what-do-your-pt-ptt-and-inr-results-mean-3157005_V2-012-a23ffe57b301411fa13d2d3a3e32c630.png)
