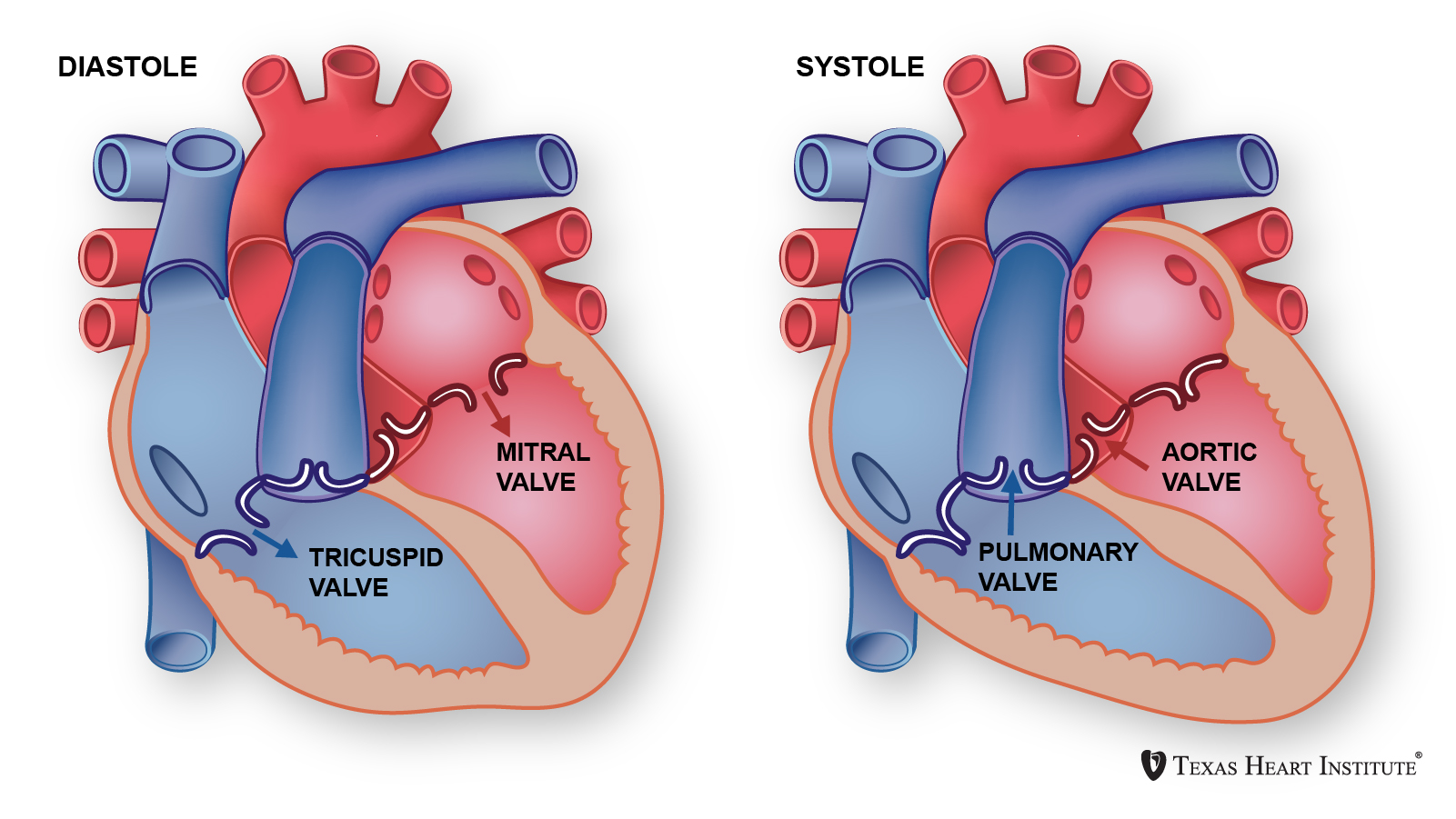
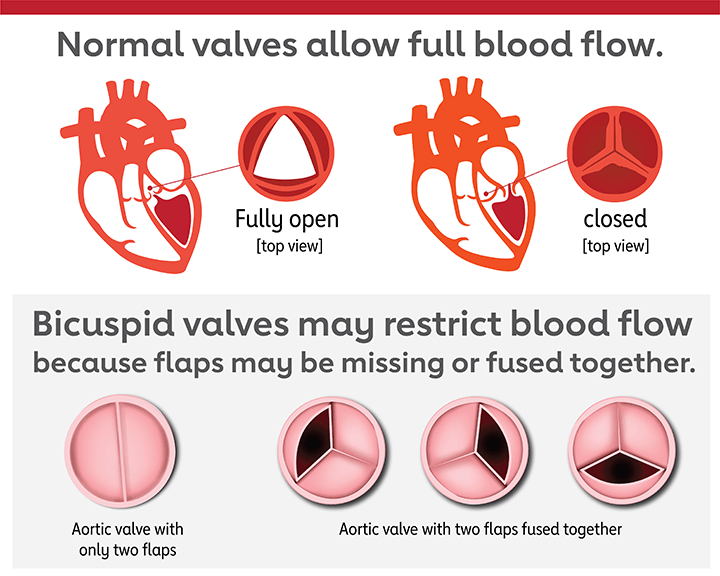
Normally sound waves received by the external and middle ear are conveyed to the fluid in the cochlea of the inner ear. This damage can involve either the cochlea or hearing nerve pathways or it can encompass both aspects of the.
 Sensorineural Hearing Loss In Adults Ppt Video Online Download
Sensorineural Hearing Loss In Adults Ppt Video Online Download
Sensorineural hearing loss SNHL is caused by damage to these special cells or to the nerve fibers in the inner ear.
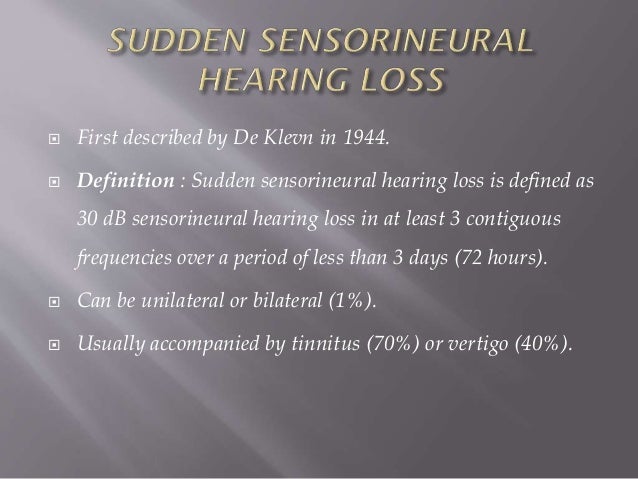
Sensorineural hearing loss definition. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear. Or the neural pathways of the. Sudden bilateral sensorineural hearing loss following postpartum hemorrhage.
Soft sounds may be hard to hear. It is the cause of more than 90 percent of. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss SSNHL defined as sudden idiopathic usually unilateral deafness developed in most within 72 hours in previously healthy person.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Definition What is sensorineural hearing loss. A sensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss. As defined it is one type of hearing loss the root cause of which is found in the vestibulocochlear nerve or Cranial.
It occurs when you lose your hearing very quickly typically only in one ear. If you have a student with such hearing. Sudden deafness frequently affects only one ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss SNHL is caused by damage to the structures in your inner ear or your auditory nerve. In this hearing loss or deafness main cause presents in the sensory organ Cochlea of the inner ear or neutral part of the inner ear or the vestibulocochlear nerve. Sometimes the hearing loss is caused by damage to.
It normally affects both ears. Sensorineural hearing loss is associated with some pathological change in structures within the inner ear or in the acoustic nerve. What is sensorineural hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss caused by a problem in the inner ear the brain or the nerve that connects the brain to the inner ear. Problems with the nerve pathways from your inner ear to your brain can also cause SNHL. SSHL happens because there is something wrong with the sensory organs of the inner ear.
It results from the damage of the tiny hair cell in the inner ear. Sudden sensorineural inner ear hearing loss SSHL commonly known as sudden deafness is an unexplained rapid loss of hearing either all at once or over a few days. Having sensorineural hearing loss means there is damage either to the tiny hair cells in your inner ear known as stereocilia or to the nerve pathways that lead from your inner ear to the brain.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss SSHL is also known as sudden deafness. What is sudden deafness. A sensorineural hearing loss is where there is damage to the hair cells present in the cochlea which is the hearing organ.
Sensorineural hearing loss that due to a defect in the inner ear or the acoustic nerve. Sensorineural hearing loss or SNHL happens after inner ear damage. Sensorineural Hearing Loss occur as a result of the loss of neural inputs death of nerve cells that connect the eardrum to the brain.
This is the most common cause of hearing loss.

/1066910-top-depression-symptoms-5ae724e38023b90036653091.png)