Individuals who have marked deficits in social communication but whose symptoms do not otherwise meet criteria for autism spectrum disorder should be evaluated for social pragmatic. Revised diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5 A.
 Ppt Diagnostic Criteria For Autism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6719288
Ppt Diagnostic Criteria For Autism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6719288
A total of six or more items from 1 2 and 3 with at least two from 1 and one each from 2 and 3.
Asd diagnostic criteria. Reprinted with permission from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition Copyright 2013. In order to have a diagnosis of Autism an individual must satisfy the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5. DSM-5 criteria for autism diagnosis Professionals diagnose autism spectrum disorder on the basis of difficulties in two areas social-communication and restricted repetitive andor sensory behaviours or interests.
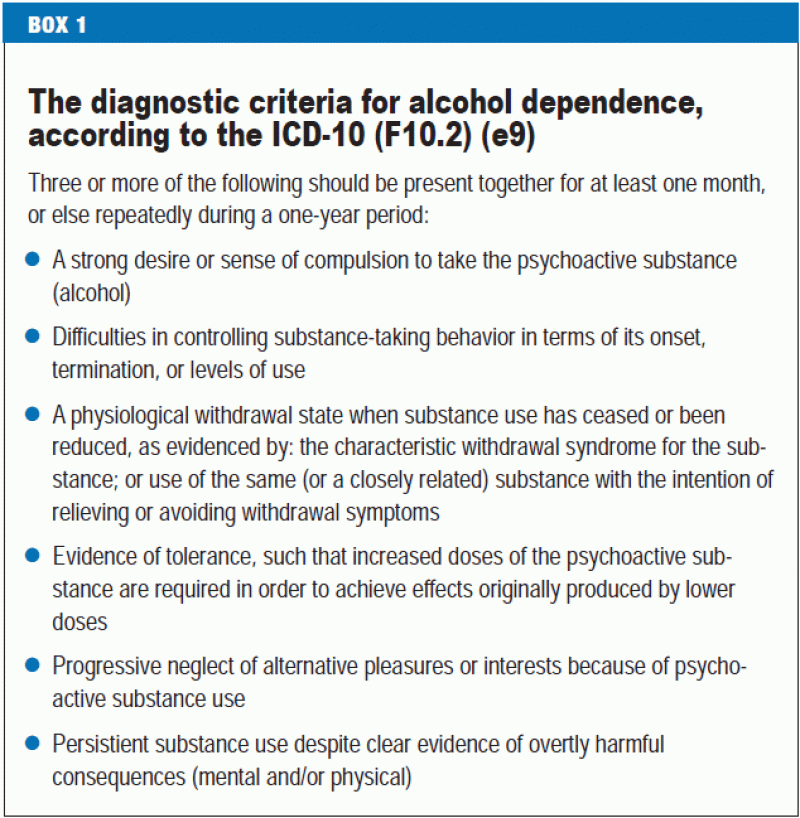
Once a suspicion is raised the diagnosis is dependent on further assessment by an individual or team specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder ASD. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts as. DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Autism Spectrum Disorder 29900 F840 A.
These create the foundation for diagnostic tools such as the DISCO Diagnostic Interview for Social and Communication Disorders the ADI-R Autism Diagnostic Interview - Revised the ADOS Autism Diagnostic. To be diagnosed with ASD an individual must meet all three of the following criteria. ASD occurs in all racial and ethnic groups and across every socioeconomic status level.
While reviewing the criteria it is important to keep in mind the wide heterogeneity of symptoms severity and clinical presentations that characterize children with ASD. To be diagnosed with ASD children must. Only well-qualified trained professionals can issue an autism diagnosis.
Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts as manifested by the following currently or by history 1. There is no single test that is diagnostic of autism. If you go for an autism assessment the clinician will use a diagnostic tool to help decide whether you are autistic or not.
Difficulties in social emotional reciprocity including trouble with social approach back and forth conversation sharing interests with others and expressingunderstanding emotions. Diagnostic criteria introduced in the fifth edition in May 2013 are no exception. In this article you will find the diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder under both DSM-5 and the DSM-IV.
These criteria encompass clinical signs pertaining to the two primary areas of impairment seen in ASD. Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnosis of autistic disorder Aspergers disorder or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. These tools include the DISCO Diagnostic Interview for Social and Communication Disorders the ADI-R Autism Diagnostic Interview - Revised the ADOS Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule and 3Di Developmental Dimensional and Diagnostic Interview.
Todays diagnostic criteria comes from the the DSM-5 which clinicians have continued to expand since 1980 and defines ASD as a developmental disorder that causes Persistent deficits in. Qualitative impairment in social interaction as manifested by at least two of the following. Boys are about four times more likely to have ASD than girls.
See the full criteria for ASD from the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition. Diagnostic criteria - a guide for all audiences. Diagnostic manuals ICD-10 and DSM-5 set out the criteria for autism to be diagnosed.
Below plus at least two of four types of restricted repetitive behaviors see B1. Have difficulties in both areas. To meet diagnostic criteria for ASD according to DSM-5 a child must have persistent deficits in each of three areas of social communication and interaction see A1.
The American Psychiatric Association has outlined diagnostic criteria for autism in its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM. DSM IV Criteria for Diagnosing Autistic Disorder.